H5n1 who – With H5N1 making headlines, this article delves into the complexities of this virus, exploring its origins, transmission, and impact on humans, animals, and public health.
H5N1, a highly pathogenic avian influenza virus, has raised global concerns due to its potential to cause severe respiratory illness in both birds and humans.
H5N1 Overview
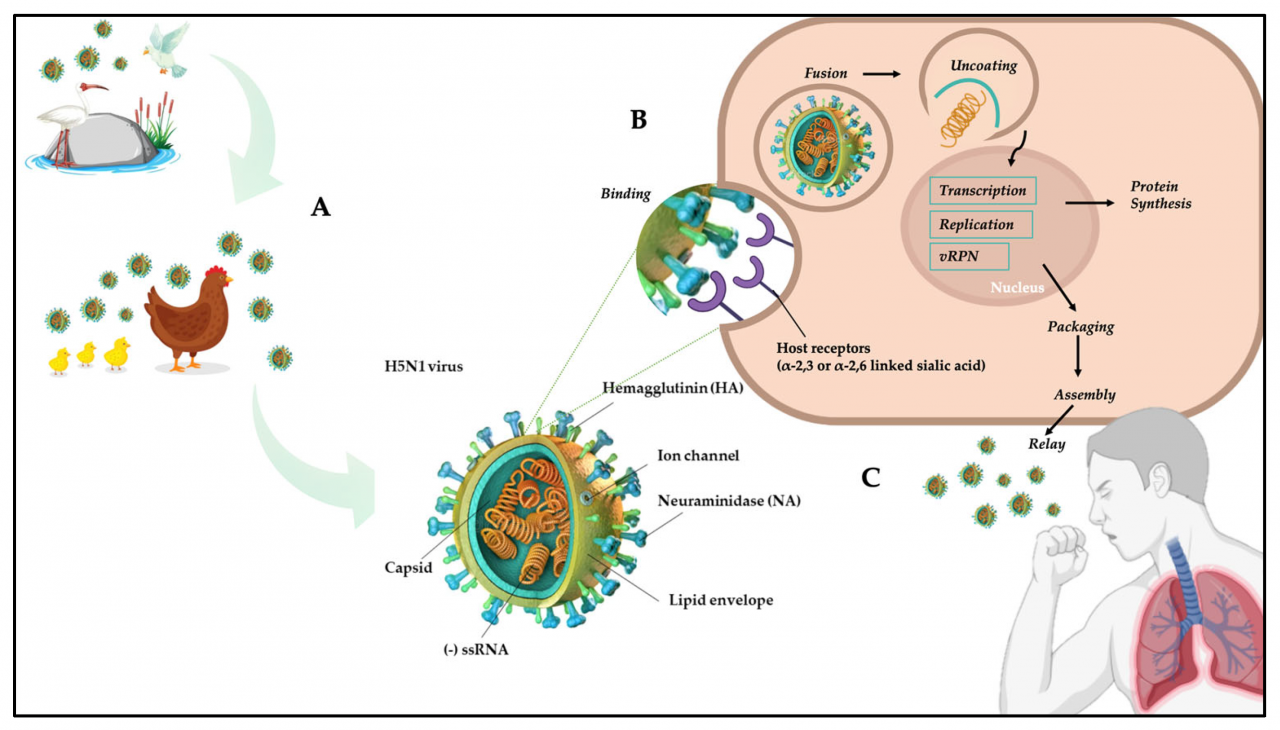
H5N1 is a highly pathogenic avian influenza virus that belongs to the Orthomyxoviridae family. It is characterized by its segmented, single-stranded RNA genome and a surface protein called hemagglutinin (H) and neuraminidase (N). The H5N1 strain has caused significant outbreaks in poultry and has also been responsible for sporadic infections in humans.
The virus originated from wild aquatic birds, particularly migratory waterfowl, and has evolved over time to infect domestic poultry. The first major outbreak of H5N1 in poultry occurred in Hong Kong in 1997, leading to the culling of millions of birds.
Since then, the virus has spread to various parts of the world, causing significant economic losses in the poultry industry.
H5N1 infection in humans can occur through close contact with infected poultry or contaminated surfaces. Symptoms typically include fever, cough, sore throat, muscle aches, and respiratory distress. In severe cases, the virus can lead to pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and multiple organ failure.
H5N1 in Humans

Human infections with H5N1 are relatively rare, but they can be severe. The virus has a high mortality rate, with approximately 60% of reported cases resulting in death. Risk factors for severe H5N1 infection include older age, underlying medical conditions, and exposure to a large amount of virus.
Most human cases of H5N1 have been reported in Southeast Asia, particularly in countries such as Cambodia, Indonesia, and Vietnam. However, sporadic cases have also occurred in other parts of the world, including Europe, Africa, and North America.
Public health interventions, such as antiviral treatment and infection control measures, have been implemented to mitigate the impact of H5N1 in humans. However, the development of a safe and effective vaccine remains a priority.
H5N1 in Animals
H5N1 has a significant impact on poultry populations. Infected birds can develop severe respiratory symptoms and often die within a few days. The virus can spread rapidly through poultry flocks, leading to mass mortality and economic losses.
Outbreaks of H5N1 in poultry have occurred in various parts of the world, including Asia, Europe, and North America. The virus has caused significant disruptions in the poultry industry, leading to trade restrictions and the culling of millions of birds.
Surveillance, control, and prevention measures are essential to mitigate the spread of H5N1 in animals. These measures include biosecurity practices, vaccination of poultry, and early detection and reporting of outbreaks.
Public Health Implications
H5N1 is a virus with pandemic potential. It has the ability to cause severe disease in humans and can spread rapidly through poultry populations. The virus has been shown to undergo genetic mutations that could potentially increase its transmissibility and virulence.
Public health authorities are concerned about the possibility of a human influenza pandemic caused by H5N1. Such a pandemic could have significant global health and economic consequences.
Monitoring, detection, and response to H5N1 outbreaks are essential to mitigate its public health impact. Public health interventions, such as vaccination, antiviral treatment, and infection control measures, are crucial to protect human populations.
Research and Development: H5n1 Who
Ongoing research efforts are focused on understanding H5N1, developing vaccines, and improving treatment strategies. Scientists are studying the genetic makeup of the virus, its transmission dynamics, and its virulence factors.
Research is also underway to develop effective vaccines against H5N1. Several candidate vaccines have shown promise in animal studies, but further research is needed to evaluate their safety and efficacy in humans.
In addition, researchers are exploring new antiviral drugs and treatments for H5N1 infection. The goal is to develop therapies that can effectively combat the virus and reduce its severity in humans.
Closure
Understanding H5N1 is crucial for developing effective surveillance, prevention, and control measures to mitigate its impact on human and animal health, as well as global food security.