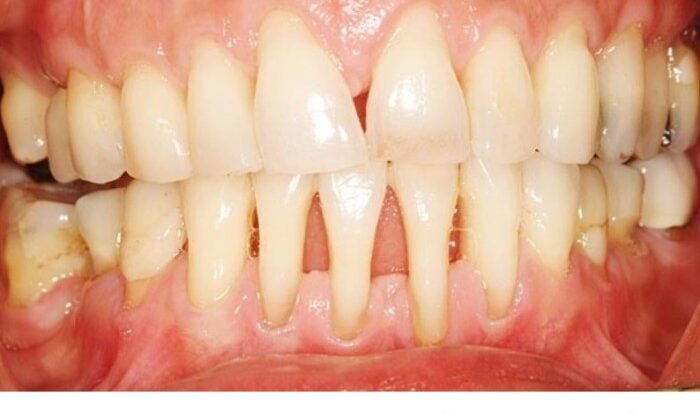
Are you tired of gum disease wreaking havoc on your oral health? Fear not! Discover how to cure gum disease without a dentist. This guide will empower you with natural remedies, home care techniques, and lifestyle modifications to restore your gums to their former glory.
Natural Remedies: How To Cure Gum Disease Without A Dentist

Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common condition that affects the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. It can range from mild inflammation to severe infection and bone loss. While professional dental care is essential for treating gum disease, several natural remedies can complement dental treatments and support oral health.
Herbs
Herbs have been used for centuries to treat various ailments, including gum disease. Some of the most effective herbs for gum disease include:
- Aloe vera:Aloe vera contains anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties that can help soothe inflamed gums and reduce bacterial growth.
- Green tea:Green tea is rich in antioxidants that can help protect the gums from damage caused by free radicals.
- Turmeric:Turmeric contains curcumin, a compound with potent anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties.
- Echinacea:Echinacea has immune-boosting properties that can help the body fight off bacterial infections.
Essential Oils
Essential oils are concentrated plant extracts that possess various therapeutic properties. Some essential oils that can be beneficial for gum disease include:
- Tea tree oil:Tea tree oil has strong antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce gum inflammation and kill bacteria.
- Peppermint oil:Peppermint oil has a cooling and numbing effect that can help relieve gum pain and inflammation.
- Clove oil:Clove oil has antibacterial and antiseptic properties that can help kill bacteria and prevent gum infections.
Dietary Supplements
Certain dietary supplements can also support gum health and complement natural remedies. Some of the most beneficial supplements for gum disease include:
- Vitamin C:Vitamin C is essential for maintaining healthy gums and supporting the immune system.
- Vitamin D:Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to increased risk of gum disease. Supplementation may help improve gum health.
- Probiotics:Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can help maintain a healthy balance of oral bacteria and reduce inflammation.
Note:It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before using any natural remedies or dietary supplements, as some may interact with medications or have potential side effects.
Home Care Techniques

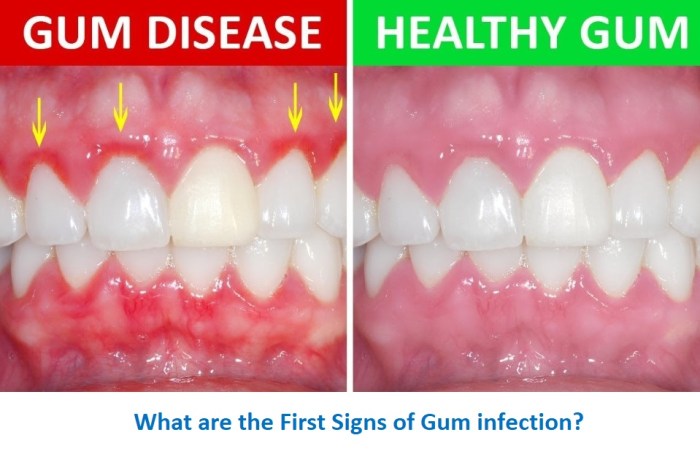
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common condition that affects the gums and the bones that support the teeth. It is caused by bacteria that form plaque on the teeth, which can lead to inflammation, bleeding, and eventually tooth loss.
While gum disease can be treated by a dentist, there are also several effective home care techniques that can help to prevent and manage the condition.
Proper Brushing and Flossing Techniques
Proper brushing and flossing techniques are essential for preventing and managing gum disease. Brushing helps to remove plaque and bacteria from the teeth, while flossing helps to remove plaque and bacteria from between the teeth and below the gum line.
Gum disease is a common problem that can lead to serious health issues if left untreated. While it’s always best to see a dentist for professional treatment, there are some things you can do at home to help cure gum disease without a dentist.
Check out this article for some helpful tips on how to cure gum disease without a dentist.
Here are some tips for proper brushing and flossing:
- Brush your teeth twice a day, for at least two minutes each time.
- Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste.
- Brush all surfaces of your teeth, including the front, back, and chewing surfaces.
- Floss your teeth once a day, using a piece of floss that is about 18 inches long.
- Floss between all of your teeth, including the back teeth.
Regular Dental Check-Ups and Professional Cleanings
Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are also important for preventing and managing gum disease. Dental check-ups allow your dentist to examine your teeth and gums for signs of gum disease, and professional cleanings help to remove plaque and bacteria from your teeth and below the gum line.
It is recommended to have a dental check-up and professional cleaning every six months.
Gum disease is a common problem that can lead to serious health issues if left untreated. While it’s always best to see a dentist for professional treatment, there are some things you can do at home to help cure gum disease.
Click here to learn more about how to cure gum disease without a dentist. You can also try using a saltwater rinse or applying a cold compress to the affected area.
Nutritional Considerations
Maintaining a healthy diet plays a pivotal role in preserving gum health. Specific nutrients and foods can promote gum well-being, while others can contribute to gum disease.
If you’re dealing with gum disease, don’t despair! There are ways to cure it without a dentist. One effective method is to try natural remedies . These remedies, such as salt water rinses or tea tree oil, can help reduce inflammation and bacteria.
Remember, gum disease is a serious issue, so if home remedies don’t improve your condition, it’s crucial to consult a dental professional.
Essential nutrients for healthy gums include:
- Vitamin C: Crucial for collagen production, which strengthens gum tissue.
- Vitamin A: Supports the production of saliva, which neutralizes acids and protects against bacteria.
- Vitamin D: Aids in calcium absorption, essential for bone and tooth health.
- Calcium: Supports bone and tooth strength, including the jawbone that anchors the teeth.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Found in fatty fish, they have anti-inflammatory properties that can benefit gum health.
Conversely, certain foods and habits can contribute to gum disease:
- Sugary foods and drinks: Feed bacteria that produce acids, damaging teeth and gums.
- Acidic foods and drinks: Can erode tooth enamel and weaken gums.
- Smoking: Damages gum tissue and reduces blood flow to the gums.
- Poor oral hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing allows plaque and bacteria to accumulate, leading to gum disease.
Lifestyle Modifications
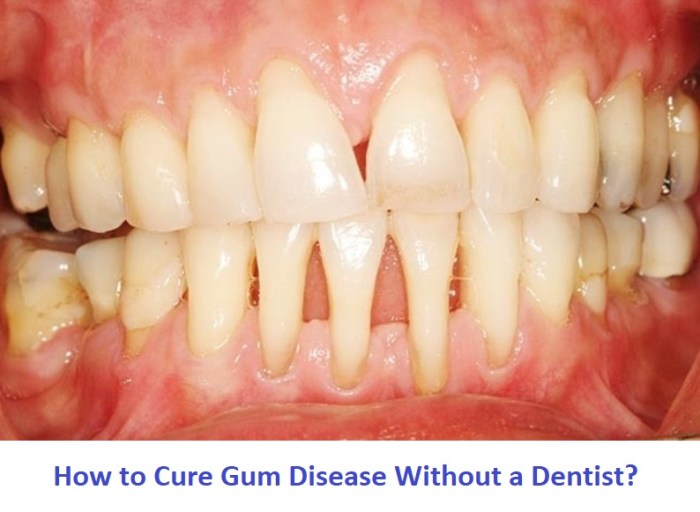
Lifestyle factors play a significant role in maintaining gum health. Certain habits and behaviors can contribute to the development and progression of gum disease. Understanding these factors and making positive lifestyle changes can help improve gum health and prevent further damage.
Some key lifestyle factors that impact gum health include smoking, stress, and poor sleep.
Smoking, How to cure gum disease without a dentist
Smoking is a major risk factor for gum disease. The chemicals in cigarettes damage the gum tissue and blood vessels, making it more susceptible to infection. Smoking also impairs the immune system’s ability to fight off bacteria, further increasing the risk of gum disease.
There are many ways to cure gum disease without a dentist, such as using mouthwash, flossing, and brushing your teeth regularly. However, if you’re looking for a more comprehensive solution, you can check out how to cure gum disease without a dentist for more information.
This website provides detailed instructions on how to cure gum disease without a dentist, so you can get your smile back on track.
Stress
Chronic stress can weaken the immune system, making the body more vulnerable to infections, including gum disease. Stress can also lead to poor oral hygiene habits, such as skipping brushing or flossing, which can further contribute to gum problems.
Poor Sleep
Getting enough sleep is essential for overall health, including gum health. When you don’t get enough sleep, your body produces more of the stress hormone cortisol, which can suppress the immune system and make it harder to fight off infections.
Poor sleep can also lead to dry mouth, which can increase the risk of gum disease.
Alternative Therapies
In addition to conventional treatments, alternative therapies can provide complementary support for gum disease management. These therapies aim to address the underlying imbalances that contribute to gum disease and promote overall well-being.
Some alternative therapies that may benefit gum health include acupuncture, yoga, and meditation.
Acupuncture
- Acupuncture involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body.
- It is believed to stimulate the body’s natural healing mechanisms, reduce inflammation, and improve blood circulation.
- Studies have shown that acupuncture can effectively reduce gum inflammation and bleeding.
Yoga
- Yoga combines physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation.
- It helps reduce stress, improve circulation, and enhance the body’s ability to fight infection.
- Regular yoga practice has been linked to improved gum health and reduced gum bleeding.
Meditation
- Meditation involves focusing the mind on a specific object or thought.
- It helps reduce stress, anxiety, and inflammation.
- Meditation has been shown to improve immune function and promote overall well-being, which can support gum health.
Conclusion
With a little effort and these practical tips, you can kiss gum disease goodbye and enjoy a healthy, radiant smile. Remember, prevention is key, so embrace these strategies and give your gums the TLC they deserve.
FAQ Overview
How long does it take to cure gum disease naturally?
The time frame for curing gum disease naturally varies depending on the severity of the condition. However, with consistent application of the techniques discussed in this guide, you can expect noticeable improvements within a few weeks.
Can I use essential oils to treat gum disease?
Yes, certain essential oils like tea tree oil and clove oil possess antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties that can aid in reducing gum inflammation and infection.
Is it possible to prevent gum disease?
Absolutely! Regular brushing and flossing, along with a healthy diet and avoiding tobacco products, can significantly reduce your risk of developing gum disease.